
The other three mechanisms appeared important to the likelihood of an intervention being successful, particularly when operating simultaneously. Though increasing the risk to offenders of being detected was assumed to be a central mechanism in deterring sexual violence, the evidence suggests that this mechanism operated only in interventions focused on gathering firewood and providing alternative fuels. Drawing on pre-existing capacity or culture in communities is an additional mechanism which should be explored. These mechanisms appeared to contribute to outcomes in multiple-component interventions, as well as those relating to gathering firewood, codes of conduct for personnel and legal interventions. Four main mechanisms appear to contribute to effective interventions: increasing the risk to offenders of being detected building community engagement ensuring community members are aware of available help for and responses to sexual violence and safe and anonymous systems for reporting and seeking help. The limited data available indicate that there are few deterrents to sexual violence in crises. It is well suited to complex interventions as it takes into account contextual factors to identify mechanisms that contribute to outcomes. The realist approach is an exploratory and theory-driven review method.

This study employed a realist review of the literature on interventions with the aim of identifying the mechanisms at work across the range of types of intervention.
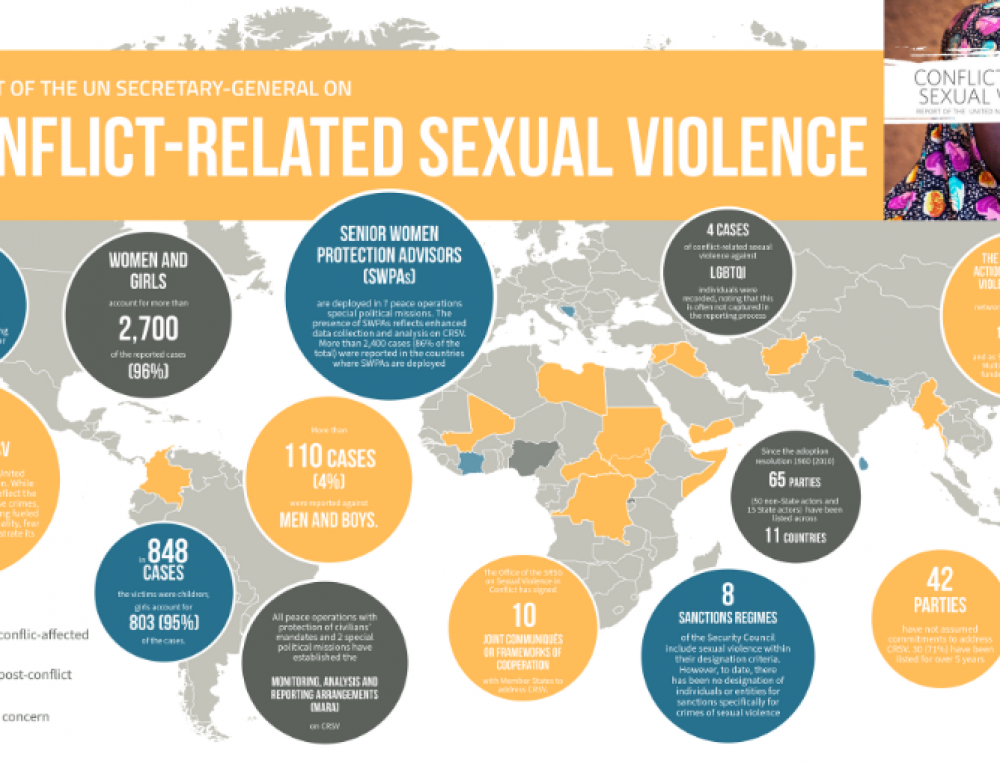
The limited evidence in literature on interventions in this field suggests a need for alternatives to traditional review methods, particularly given the challenges of undertaking research in conflict and crisis settings. Sexual violence is recognised as a widespread consequence of armed conflict and other humanitarian crises.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
